Speech Entrainment Detection
Deep neural networks for detecting speech entrainment in conversational interactions
Overview
This project focuses on developing deep neural network architectures for automatically detecting speech entrainment phenomena in conversational interactions. Speech entrainment refers to the automatic and unconscious tendency for speakers to adapt their speech patterns to match those of their conversation partners. For example, a speaker of American English may unconsciously adjust their pronunciation to align with a British English speaker when he or she is traveling in the UK. This phenomenon is crucial for understanding social dynamics in communication, as it can influence perceptions of empathy, rapport, and social bonding.
Speech entrainment is also termed phonetic convergence, iterative alignment, or speech accommodation. While speech entrainment has been studied in psychology and linguistics, the use of deep learning techniques to automatically detect and analyze this phenomenon is relatively novel. This project aims to bridge this gap by leveraging advanced neural network architectures to analyze speech data and identify patterns of entrainment.
Key Features
- Siamese Recurrent Neural Network (RNN): A specialized neural network architecture designed to measure phonetic convergence in speech.
- Text-Independent Model: The Siamese RNN is designed to be text-independent, allowing it to handle variability in speaker characteristics and linguistic backgrounds.
- Scalability: The model can scale to different languages and speaker groups, making it applicable in diverse linguistic contexts.
Dataset
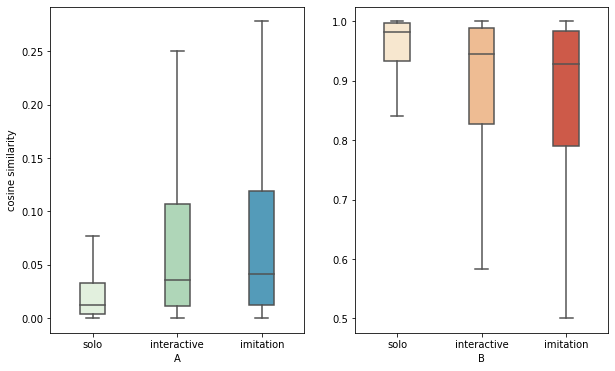
The study builds upon a specially curated dataset known as the alternating reading task (ART). This dataset includes speech samples from 58 speakers of different native languages (Italian, French, Slovak) engaged in a controlled reading task. The ART dataset has solo, interactive, and imitation conditions, allowing for a comprehensive analysis of speech entrainment across different conversational contexts.
Technical Implementation
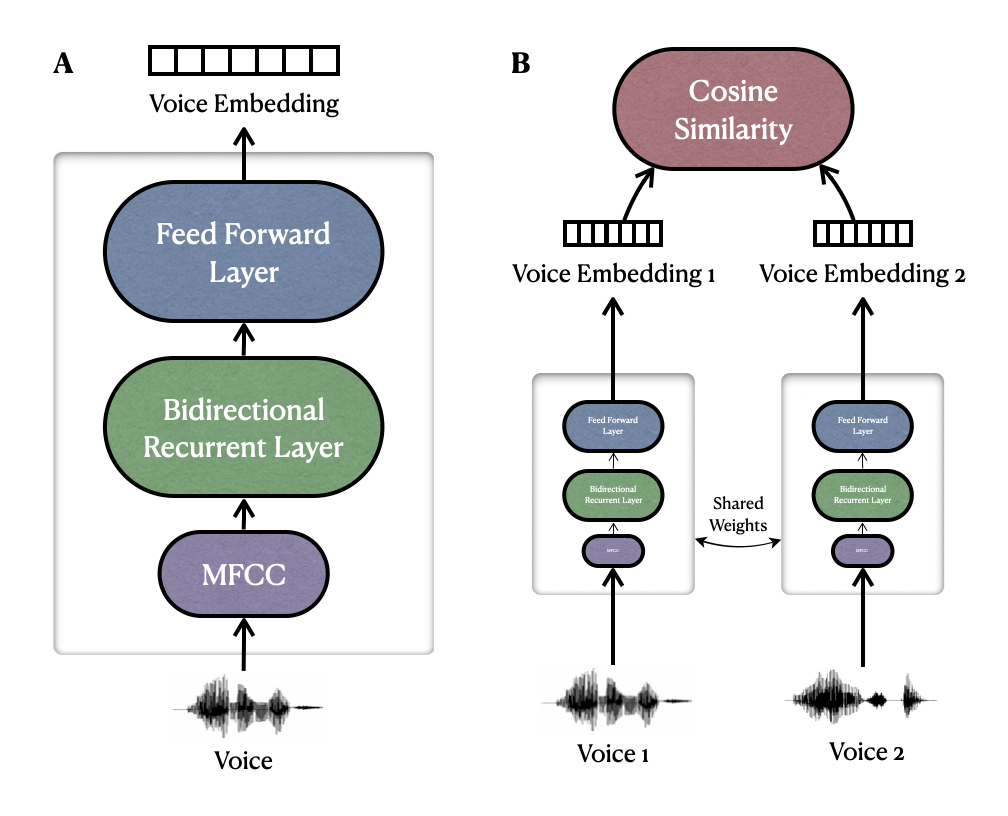
Technologies Used
- Python: Primary programming language
- TensorFlow: Deep learning framework
- Librosa: Audio processing and feature extraction
Research Impact
This work contributed to the European Union’s Conversational Brains project, advancing our understanding of how humans naturally synchronize their speech during interactions. The findings have implications for:
- Human-computer interaction design
- Speech therapy applications
- Social robotics
- Communication disorders research
Publications
Future Directions
- Extension to multimodal entrainment (visual and gestural)
- Real-time feedback systems for communication training
- Integration with conversational AI systems
- Interpretability studies to compare human and machine entrainment measurements